- Published:
- Written by: B.F.S Industries
Scaffolding Safety Inspection Checklist

FREE DOWNLOAD – B.F.S. HOLDING
Explore the full spectrum of services and industries covered by B.F.S. Holding.
Scaffolding plays a critical role in construction, maintenance, and industrial projects, but it also presents serious safety risks if not properly inspected. A well-structured scaffolding safety inspection checklist helps prevent falls, structural failures, and costly delays. This guide explains how to inspect scaffolding correctly, what to look for before each shift, and how inspections align with OSHA and international safety standards. By strictly adhering to these protocols, site managers and workers can ensure that every temporary structure is secure, minimizing the potential for life-threatening accidents. The following sections detail the necessary steps and considerations for maintaining a rigorous safety standard on any job site involving elevated work platforms.
Why Scaffolding Safety Inspections Are Essential
Scaffold-related accidents are often caused by improper assembly, missing components, or ground instability. Regular inspections ensure that scaffolds remain plumb, square, and level, reducing the risk of collapse or falls. Proper inspection routines also help contractors comply with legal safety requirements and protect workers at height. When companies like BFS Industries supply high-quality materials, the integrity of those materials must still be verified through daily checks to ensure they haven’t been compromised during assembly or use.

Beyond the immediate physical safety of the workers, routine inspections are a critical component of risk management and financial stability for a construction project. A single accident can lead to devastating stop-work orders, legal battles, and skyrocketing insurance premiums. Furthermore, the structural integrity of a scaffold is not static; it changes as loads are applied, weather conditions shift, and work progresses. Ensuring that every connection is tight and every plank is secure is the only way to guarantee that the structure will perform as intended. This proactive approach cultivates a culture of safety where every worker feels empowered to speak up if they notice something amiss, ultimately creating a more efficient and secure working environment.
When Should Scaffolding Be Inspected?
Scaffolding must be inspected before the first use, at the start of every work shift, and after any event that could affect its integrity, such as strong winds, heavy rain, modifications, or impact from equipment. In many projects, a more detailed weekly inspection is also recommended to identify gradual wear or loosening connections. The timing of these inspections is not arbitrary; it is designed to catch potential failures before workers rely on the structure for their safety. For instance, a scaffold that was perfectly safe on a Friday afternoon may have settled into the mud after a weekend of heavy rain, making a Monday morning inspection absolutely vital before anyone climbs the ladder.

It is also crucial to conduct inspections whenever the scaffold layout is altered. Even minor changes, such as moving a platform level or adjusting a guardrail, can alter the load distribution and affect the overall stability of the system. Additionally, inspections should occur following any incident where the scaffold might have been struck by machinery, such as a forklift or crane. These impact events can cause unseen damage to structural members that might not be immediately obvious without a thorough examination. Adhering to this strict schedule ensures that the scaffolding remains a reliable tool rather than a hidden hazard throughout the duration of the construction project.
Pre-Use Scaffolding Safety Inspection Checklist
Before workers climb onto a scaffold, several critical points must be checked to ensure the foundation and primary access points are secure. These include foundation stability, proper base plates or sole boards, secure connections, intact platforms, and adequate guardrails. Access points such as ladders or stair towers should be firmly attached and free of obstructions. The inspection begins at the ground level, where the competent person must verify that the ground condition can support the load of the scaffold and the workers. Mud sills or sole boards must be used on softer ground to distribute the weight effectively and prevent sinking or shifting, which could lead to a catastrophic collapse.
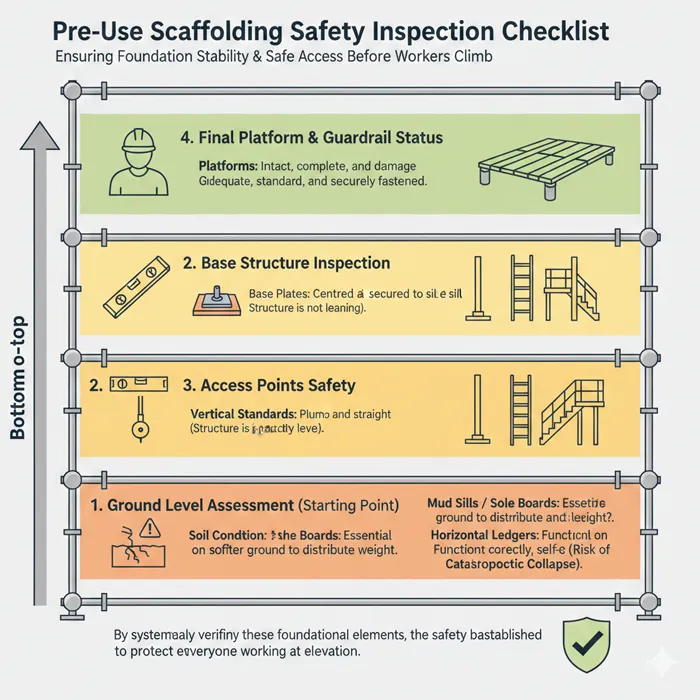
Moving upward from the base, the inspector must confirm that all base plates are centered and secured to the sill. The vertical standards needs to be checked for plumbness, ensuring the structure is not leaning, while the horizontal ledgers must be level. It is equally important to check the means of access; ladders must be free of grease or mud, and stair towers must have clear, unobstructed pathways. Gates and hatches used for access must function correctly, closing automatically to prevent accidental falls. By systematically verifying these foundational elements before anyone steps foot on the platform, the site safety team establishes a baseline of security that protects everyone working at elevation.
Structural and Component Inspection Points
All scaffold components must be inspected for damage, corrosion, or deformation. Standards, ledgers, braces, and couplers should be correctly installed and tightened. Systems such as the cuplock scaffolding system or ringlock scaffolding system require special attention to locking mechanisms to ensure they are fully engaged. A visual check should confirm that there are no bent or crushed tubes, as even minor deformities can significantly reduce the load-bearing capacity of the steel. Rust is another enemy of structural integrity; surface rust might be acceptable, but deep pitting that compromises the thickness of the metal requires the immediate removal of the component from service.
For modular systems, the specific connection points differ but the principle remains the same. In a cuplock system, the top cup must be hammered tight against the ledger blade to ensure a rigid connection. Similarly, for a ringlock scaffolding system, the wedge must be driven fully into the rosette to create a secure joint. Inspectors must also check that bracing is present and installed according to the design plan, as diagonal braces are essential for preventing the scaffold from swaying or racking. It is also vital to understand the Difference Between Shoring and Scaffolding during inspection; while they may look similar, their components and load ratings differ, and mixing them inappropriately can lead to structural failure.
Platform, Guardrail, and Fall Protection Checks
Scaffold platforms must be fully decked, properly supported, and free from excessive gaps. Guardrails, midrails, and toe boards should be installed at required heights. Where necessary, personal fall arrest systems must be compatible with the scaffold design and inspected according to manufacturer guidelines. The working platform itself is the stage upon which all activity happens, so it demands rigorous scrutiny. Planks must be inspected for cracks, rot, or chemical damage, and they must be cleated or secured to prevent uplift from wind. The gap between planks should be minimal to prevent tools or materials from falling through, and the space between the platform and the work face should be no more than 14 inches unless a fall protection system is in use.
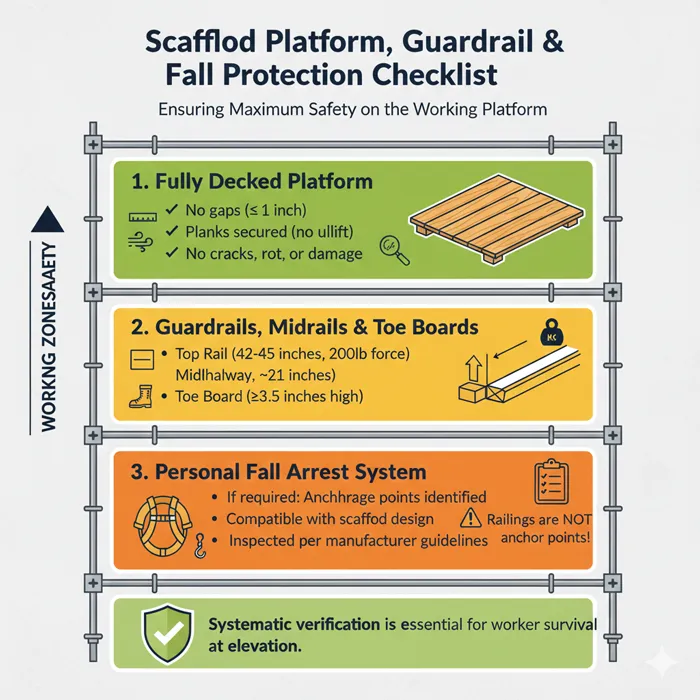
Guardrails serve as the primary means of fall prevention and must be present on all open sides of the platform. The top rail needs to be capable of withstanding a significant downward or outward force, typically 200 pounds, while the midrail prevents workers from slipping underneath. Toe boards are equally important as they prevent equipment and debris from being kicked off the edge onto workers below. If the scaffold design requires workers to use personal fall arrest systems, the anchorage points must be identified and verified by a qualified person. A simple railing is often not rated as an anchor point, so clarity on where to hook off is essential for worker survival in the event of a slip.
OSHA Scaffolding Inspection Requirements
According to OSHA, scaffolds must be inspected by a competent person before each work shift. This includes verifying load capacities, ensuring scaffolds are erected on stable foundations, and confirming that no unauthorized alterations have been made. Understanding OSHA scaffold inspection requirements helps avoid violations and improves overall site safety. The term “competent person” is specific in this context; it refers to someone who is capable of identifying existing and predictable hazards and has the authorization to take prompt corrective measures to eliminate them. This individual must be knowledgeable about the specific type of scaffold being used and the regulations governing it.
OSHA regulations mandate that the inspection covers every aspect of the scaffold assembly, from the soil it sits on to the topmost guardrail. The inspector must ensure that the scaffold is not loaded beyond its intended capacity, which includes the weight of the workers, their tools, and the materials being stored on the platform. Furthermore, the inspection must verify that the scaffold components are not being mixed effectively, as components from different manufacturers often have different tolerances and strength ratings. Failure to adhere to these strict federal guidelines can result in severe financial penalties for the construction company, but more importantly, it places the workforce in immediate physical danger. Compliance is not just about avoiding fines; it is about preserving human life.
Common Scaffolding Hazards Identified During Inspections
Frequent hazards include loose planks, missing guardrails, improper bracing, and unstable ground conditions. Overloading scaffolds with materials or workers is another major risk. Identifying these issues early through routine inspections significantly reduces accident potential. One of the most pervasive issues found on job sites is the unauthorized modification of the scaffold structure. Workers from various trades may remove a brace to pass materials through or take down a guardrail for easier access, neglecting to replace them. These temporary gaps in the safety system can create deadly traps for the next person who walks the deck.
Another common hazard is the accumulation of debris and materials on the platform. Scaffolds are designed for work, not storage, and piling heavy pallets of bricks or equipment can easily exceed the load limits of the decking or the frame itself. This clutter also creates serious tripping hazards in an environment where a stumble can be fatal. Environmental hazards also play a role; ice, snow, or mud on the planks can make footing treacherous. During the inspection, the competent person must look for overhead power lines as well, ensuring that the scaffold maintains a safe clearance distance to prevent electrocution. Recognizing and mitigating these common risks is the core purpose of the daily walkthrough.
Documentation and Scaffold Inspection Reports
Maintaining proper inspection records is a best practice on professional construction sites. Scaffold inspection reports should include inspection dates, identified issues, corrective actions, and the name of the competent person conducting the inspection. Proper documentation supports safety audits and regulatory compliance. A tagging system is often used in conjunction with written reports; a green tag indicates the scaffold is safe for use, a yellow tag implies caution or special requirements (like harness use), and a red tag signifies the scaffold is unsafe and must not be used. These visual indicators provide immediate communication to everyone on the site regarding the status of the structure.
The written log serves as a legal document that proves the company exercised due diligence in maintaining a safe workplace. In the event of an accident or an OSHA audit, these records demonstrate that inspections were conducted timely and that any defects noted were repaired before work resumed. The report should be detailed, noting specific locations of defects and the exact nature of the repair. It is helpful to treat these documents not just as paperwork, but as a historical record of the site’s safety culture. consistently good records often correlate with safer sites, while erratic or missing logs can be a warning sign of deeper systemic issues in safety management.
Choosing the Right Scaffolding System for Safer Inspections
Modern scaffolding systems are designed to improve stability and simplify inspections. Understanding options through resources like best scaffolding systems or technical references such as a cuplock scaffold manual helps project managers select systems that enhance both safety and efficiency. Different projects require different solutions; for instance, a complex industrial shape might be best served by a ringlock system due to its flexibility, while a straightforward facade work might be faster with a frame scaffold. Selecting the correct system from the outset reduces the likelihood of ad-hoc modifications that often lead to safety violations.
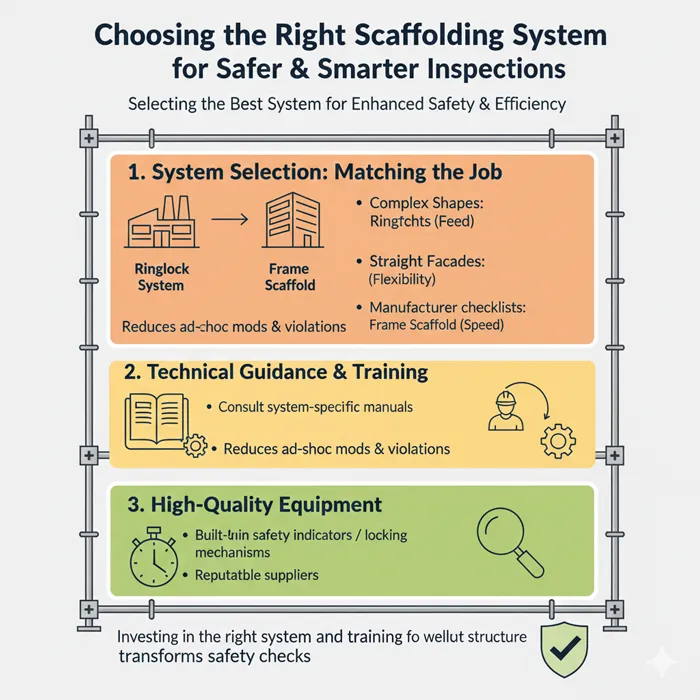
When managers consult a detailed cuplock scaffold manual or similar technical guides, they ensure that the assembly and inspection crews have clear criteria for what “correct” looks like. Manufacturers often provide specific inspection checklists tailored to their systems, which can be more effective than a generic list. Furthermore, high-quality systems from reputable suppliers often feature built-in safety indicators or locking mechanisms that are easy to visually verify. By investing in the best scaffolding systems available and ensuring the team is trained on the specific nuances of that equipment, companies can streamline the inspection process. This ensures that safety checks are not a burden, but a quick and effective confirmation of a well-built structure.
Conclusion
A detailed scaffolding safety inspection checklist is essential for preventing accidents and maintaining compliance on construction sites. By conducting daily and periodic inspections, addressing hazards promptly, and using reliable scaffolding systems, contractors can create safer working environments and reduce the risk of serious incidents. Safety at height is a continuous process that requires vigilance, knowledge, and a commitment to following established protocols every single day.
FAQ
1- How often should scaffolding be inspected?
Scaffolding should be inspected before first use, daily before each work shift, and after any event that could affect its stability or safety.
2- Who is responsible for scaffold inspections?
A competent person, as defined by OSHA, is responsible for inspecting scaffolding and its components before each work shift.
3- What is the most important pre-use check for scaffolding?
Verifying that the scaffold is erected on a stable foundation and is plumb, square, and level is one of the most critical pre-use checks.


